Welcome to the Python Trending Weekly, a weekly newsletter about Python, AI and general programming techniques, with the majority links in English and a small portion in Chinese.
The original version of the weekly was written in Chinese. What you are reading here is mostly translated by LLMs.
Substack Channel : Click to subscribe
🦄Articles & Tutorials
A report released last year by agencies including CISA and NSA listed C#, Go, Java, Python, Rust, and Swift as memory-safe languages. This PSF article discusses Python's work on memory safety, including sandboxing the underlying code, migrating from C to Rust, and using compiler options to harden the C code builds.
The author of the article is one of the core maintainers of Requests. He listed several places where the library did poorly and also pointed out many reasons why he wanted to improve it but didn't. The epilogue says: "the project feels dead". It's heartbreaking. This weekly issue 26 shared an apology from KR, the author of the library. However, there was little response in the community. Later, I saw that KR lost his job, and I felt even worse from the tweet that he was in a bad mental state. (Contributed by @frostming90)
Last issue, we shared the uv library, which can replace pip. Have you used it? How do you feel about it? The author of the article gave positive feedback and shared some before-and-after comparisons of his configuration files.
Python generators are useful for saving memory. This article uses clear examples to compare the memory usage of two different approaches, allowing us to appreciate the benefits of generators. Additionally, the article highlights some usage pitfalls to avoid.
This article discusses some advanced techniques for scraping the web, including topics such as how to better handle cookies and custom request headers, what TLS fingerprinting is and how to avoid it, common HTTP request headers to be aware of, how to integrate exponential backoff retries when making HTTP requests, and more.
How are two combinations of web development frameworks used, and what are their advantages and disadvantages? This article implements the same functionality with these two combinations, analyzes the differences between the two technology stacks, and provides a comparison checklist to help us make better technology choices.
This article is written by Wes McKinney, the author of the pandas library and the book Python for Data Analysis. He reviews what he has done and the changes he has made in the field of data science since 2008, and analyzes and thinks about the future trends of modularity, interoperability, and composability.
The author benchmarked SQLite with different major configurations and also compared the performance between SQLite and PostgreSQL. In short, enabling WAL mode, using IMMEDIATE transactions, synchronous=NORMAL, and memory-mapped I/O have little impact on the throughput.
The article introduces how Python's latest JIT is implemented, and the author tried to install the development version and then compared its performance with the version without JIT. Currently, the performance of the JIT version is slower than the normal version, and the official team still needs to continue to optimize it.
A detailed tutorial on web scraping, introducing how to use libraries like BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Selenium to achieve web scraping, and how to overcome challenges like complex web pages, rate limiting, anti-scraping, and dynamic JavaScript.
Wave is a company with only 70 engineers but valued at $1.7 billion. Its product is just a standard CRUD application, built on a Python monolith architecture on top of Postgres. The article explains why they chose such an architecture, the rationality of such a choice, and the related challenges they overcame and the technical solutions they adopted in order to maintain it.
A very in-depth and long article that delves into "concurrency", explaining how a single-threaded server can handle millions of tasks through asynchronous IO and event-driven programming. It discusses various approaches and tools for implementing concurrency, and the implementations in different programming languages. The article contains many animations to help readers understand.
🎁 Python Trending Weekly 🎁 organizes its content into seasons, with every 30 issues forming a season. The highlights from the first season have been compiled for your convenience. You can access them online here (Chinese).
🐿️Projects & Resources
This is a CLI tool to seamlessly copy data between any databases with a single command. It supports incremental loading: append, merge, and delete+insert modes. (1.3K stars)
A command-line tool for managing the PATH environment variable on your operating system, with typical features including: filtering directories, identifying and cleaning up invalid configurations, dumping PATH to JSON, creating new environment variables, and counting the number of.
A full-stack web development framework featuring full-stack type checking, friendly service communication and data binding, server-side rendering, enhanced validation with static analysis for the web, and more.
Use a unified API to access large models, featuring: unified API, multi-modal support, support for 10+ large model platforms, asynchronous & streaming and concurrency, self-contained, lightweight, high-quality code. (Submitted by @wangyuxinwhy)
"The world wastes at least $100 million per year on inefficient string operations." This project replaces the native string type in programming languages to improve performance. It speeds up exact and fuzzy string matching, edit distance calculations, sorting, lazy evaluation of ranges to avoid memory allocations, and even a random string generator. (1.4k stars)
It uses a completely self-developed kernel and has the following advantages over Selenium: no webdriver features, cross-iframe element search, treats iframes as ordinary elements, can operate multiple tabs at the same time, can directly read browser cache to save pictures, can take screenshots of the entire web page, etc. (star 4.1K)
Daft: Distributed DataFrame for Python designed for the cloud, powered by Rust https://github.com/Eventual-Inc/Daft
A distributed query engine for large-scale data processing built with Rust, featuring a familiar interactive API, focus on query optimization, integrated data catalog, rich polymorphic type system, and built for the cloud. (1.4k stars)
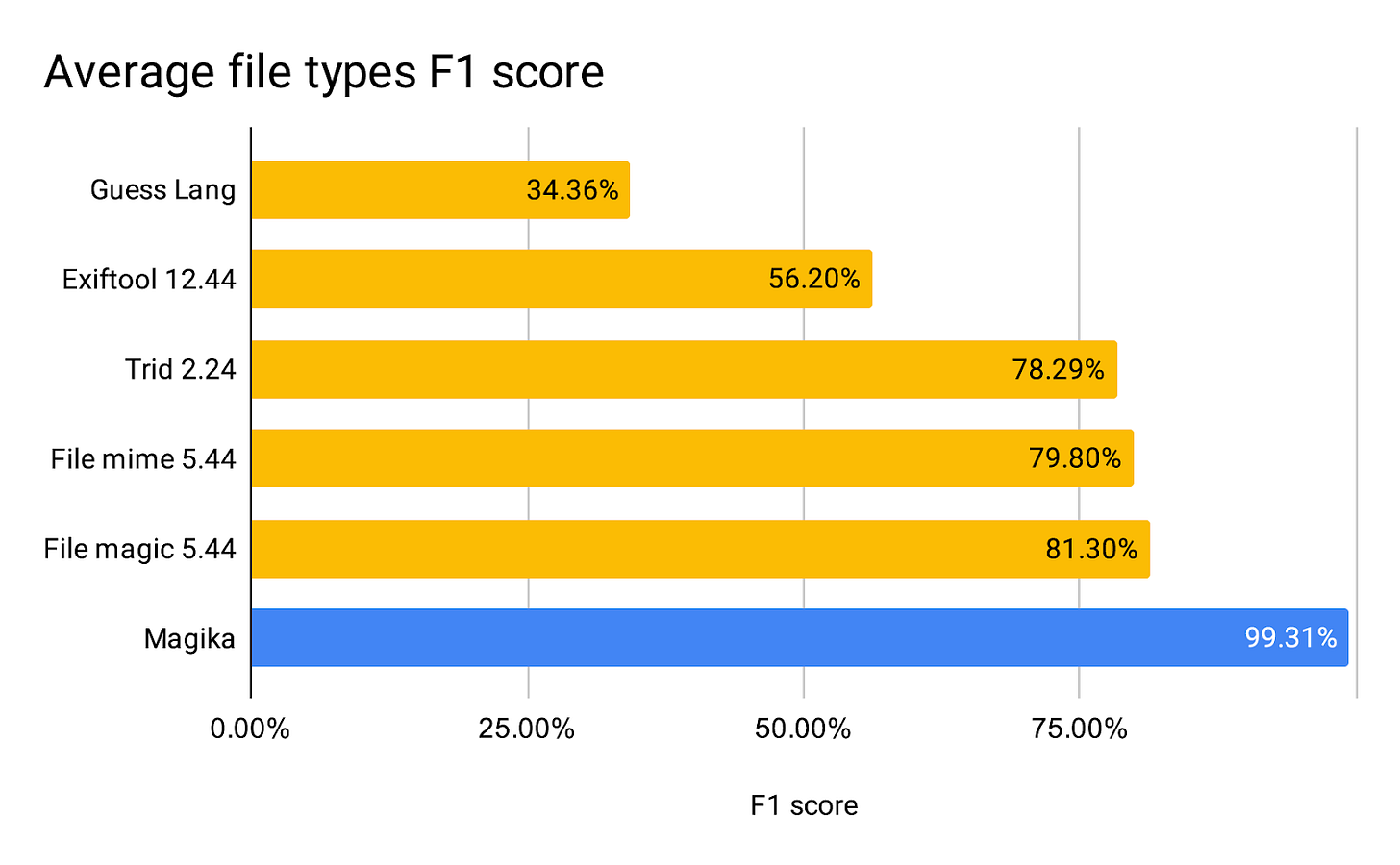
Google's latest open-source project uses AI to detect file types with 99% accuracy. Available as a Python command-line tool and API, it supports over 100 file types with an inference time of around 5 milliseconds per file. (7k stars)
frappe: Low code web framework for real world applications, in Python and Javascript (https://github.com/frappe/frappe)
A full-stack web framework with batteries included, low code, server-side with Python and MariaDB, featuring: metadata first, admin interface, roles and permissions out of the box, plugins support, task scheduler, email management, multi-tenancy, and more. (6.3k stars)
Unzip and use, run offline, no network required; comes with a high-efficiency offline OCR engine, built-in multilingual recognition library; supports multiple invocation methods such as command line, HTTP interface; screenshot OCR / batch OCR / PDF recognition / QR code. (19.4k stars)
This project is a superset of Python 3.6+ with shell primitives. It can be used as a shell and Python separately, or you can write shell in Python and Python in shell. (7.8k stars)
🐼Subscribe Welcome
Blog: Explore my independent blog where you can find a collection of original/translated technical articles over the years, along with some reflections since 2009.
Newsletter: Subscribe to my channel on Substack for a curated newsletter delivered straight to your inbox, keeping you updated on current affairs.
Github: Access the Markdown source files of this weekly digest on Github and feel free to use them for anything you have in mind!
Telegram: Beyond notifications for the weekly digest, I consider it an "extra edition," providing additional, more diverse information.
Twitter: Follow me on Twitter where my feed is filled with numerous accounts of developers and organizations in the Python community.